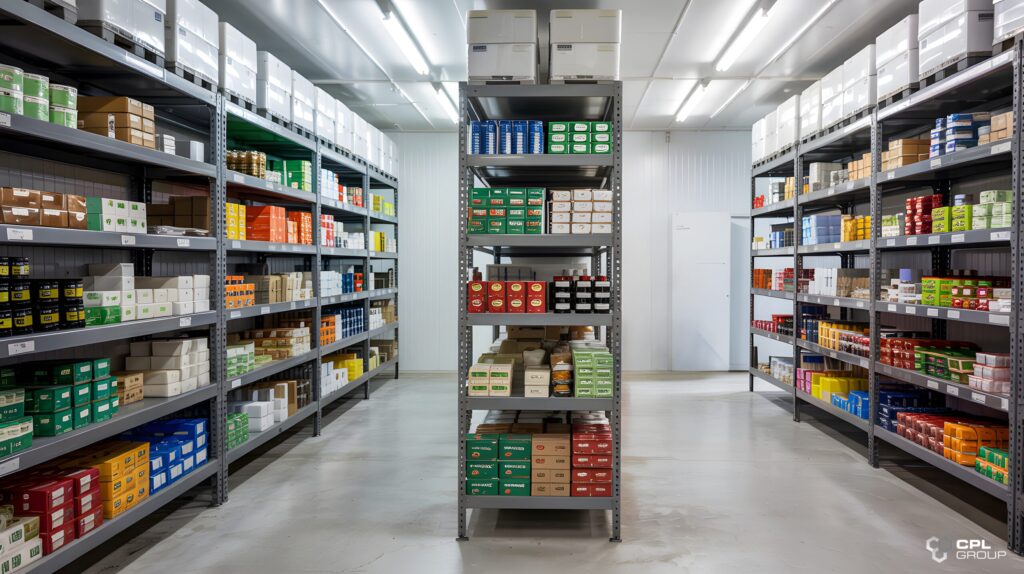
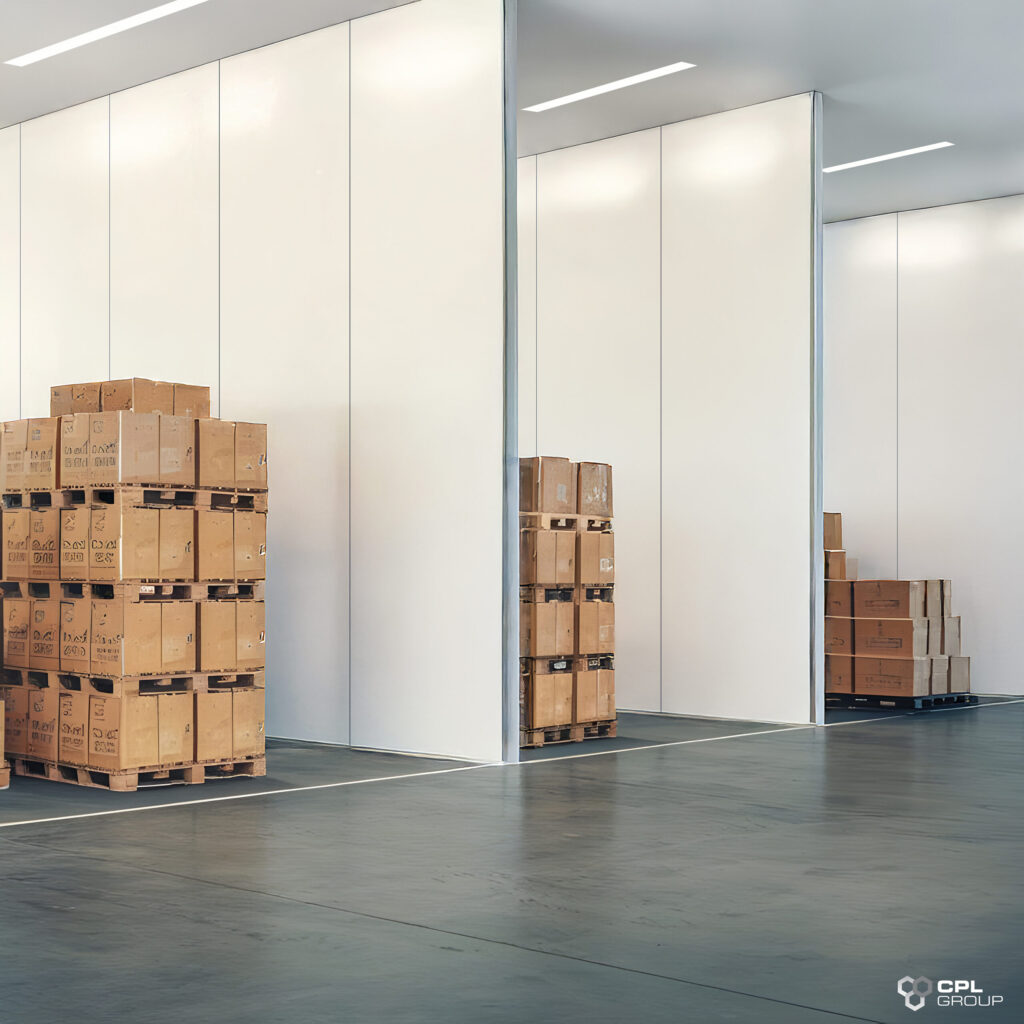
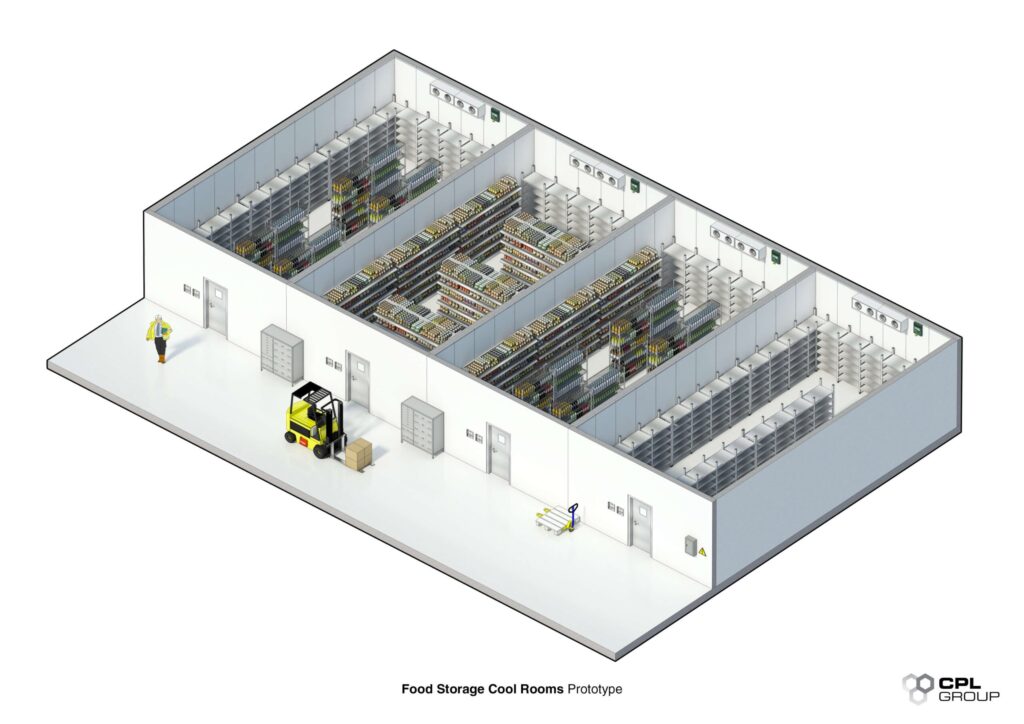
In the fast-paced world of food and beverage production, temperature control rooms play a crucial role in maintaining product quality and safety. But what goes into designing and constructing these specialized environments? Let’s explore the key considerations that industry professionals need to keep in mind.
Understanding the Basics
Temperature control rooms, essential in food and beverage processing, are specially designed spaces where temperature and humidity are precisely regulated. Before diving into the design process, it’s crucial to understand their importance in preserving product integrity and meeting stringent industry standards.
Key Design Considerations of Temperature Control Rooms for the F&B

1. Purpose and Specifications
- Identify specific needs: Determine the exact temperature and humidity ranges required for your products.
- Capacity planning: Consider current and future storage needs to avoid outgrowing the space too quickly.
2. Insulation and Vapor Barriers
- High-quality insulation: Essential for maintaining consistent temperatures and energy efficiency.
- Proper vapor barriers: Prevent moisture infiltration, which can lead to mold and compromised structural integrity.
3. Flooring
- Durable and cleanable: Choose materials that can withstand heavy traffic and frequent cleaning.
- Insulated subflooring: Prevents temperature transfer from the ground.
4. Door Systems
- Air-tight seals: Minimize temperature fluctuations during entry and exit.
- Fast-acting doors: Reduce the time the controlled environment is exposed to outside conditions.
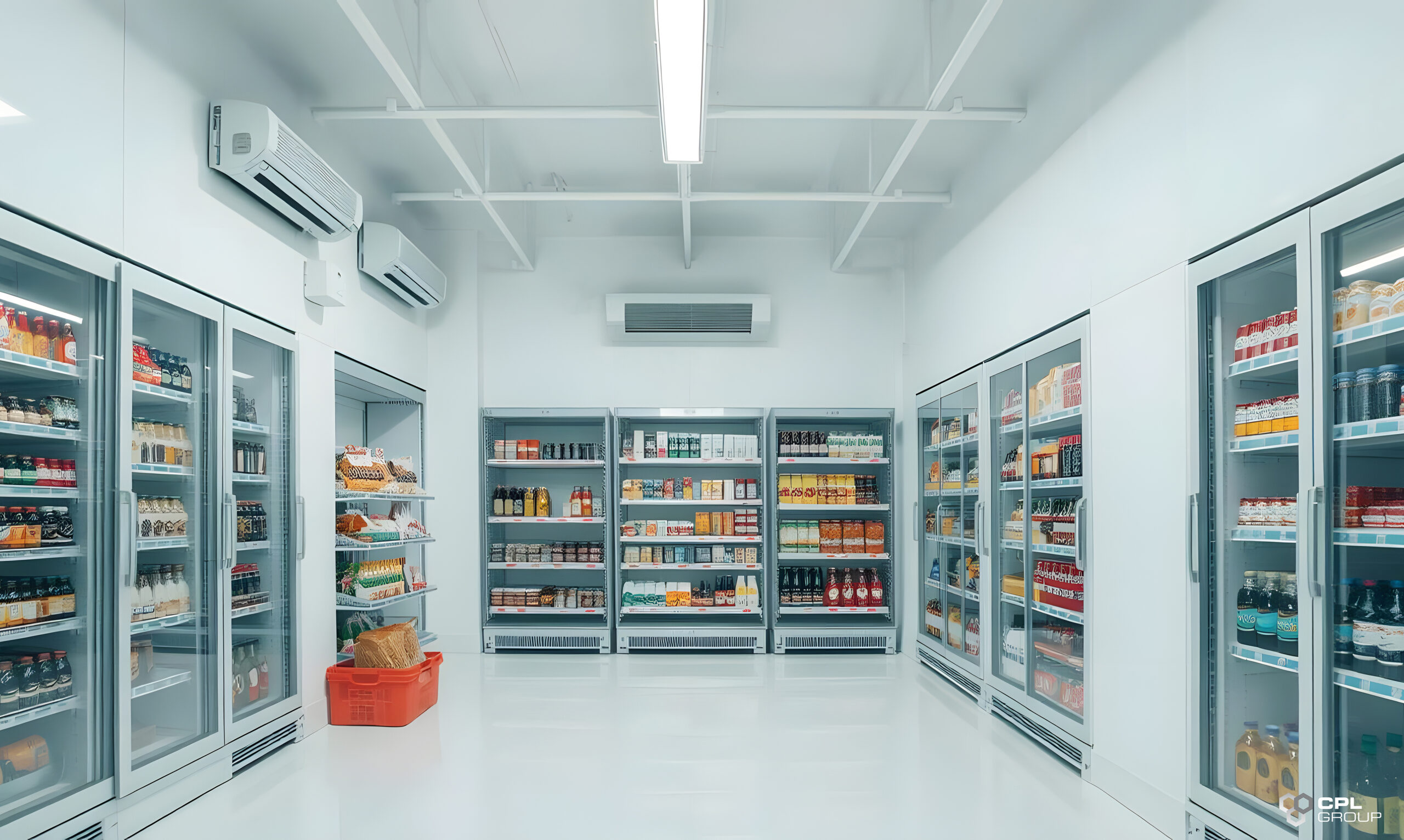
5. Lighting
- Energy-efficient options: LED lighting reduces heat generation and energy consumption.
- Proper placement: Ensure even distribution of light without creating heat pockets.
6. HVAC Systems
- Precise control: Choose systems capable of maintaining exact temperatures with minimal fluctuation.
- Redundancy: Install backup systems to prevent catastrophic failures.
7. Monitoring and Control Systems
- Real-time monitoring: Implement systems that provide constant temperature and humidity data.
- Automated alerts: Set up notifications for any deviations from set parameters.
Construction Considerations of Temperature Control Rooms
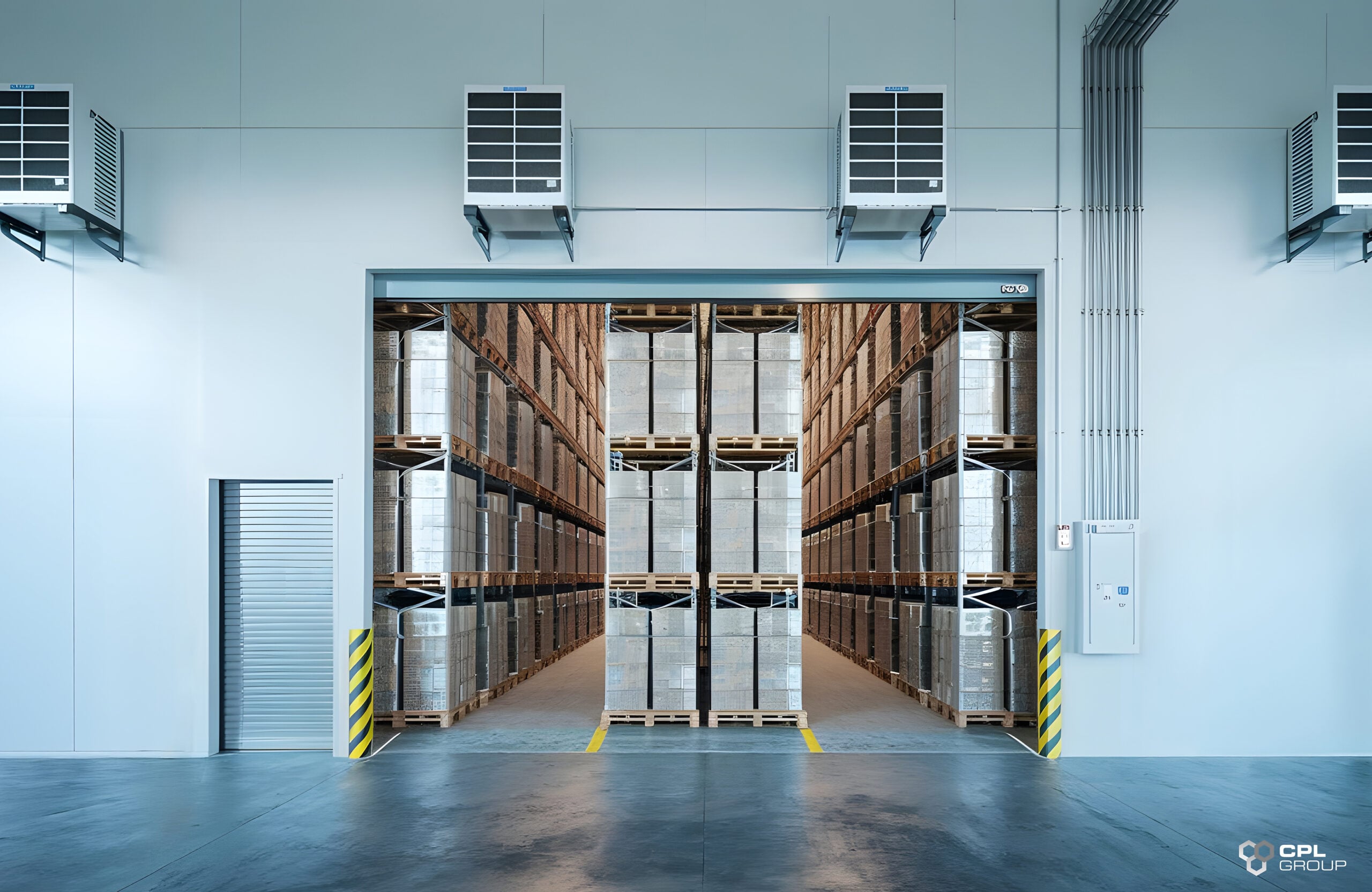

1. Site Selection
- Location: Consider proximity to production areas and loading docks.
- Structural support: Ensure the building can support the weight of the room and equipment.
2. Regulatory Compliance
- Food safety standards: Adhere to FDA, USDA, and other relevant regulatory guidelines.
- Local building codes: Ensure compliance with all local construction regulations.
3. Energy Efficiency
- Sustainable design: Incorporate energy-saving features to reduce long-term operational costs.
- Proper sizing of equipment: Avoid oversized systems that waste energy.
4. Future-Proofing
- Scalability: Design with potential future expansion in mind.
- Adaptability: Consider how the space might need to adapt to changing industry requirements.
Conclusion
Designing and constructing effective temperature control rooms requires careful planning and consideration of numerous factors. By focusing on these key areas, food and beverage industry professionals can create environments that not only meet current needs but are also prepared for future challenges and opportunities.
Investing in well-designed temperature control rooms is more than just a regulatory requirement—it’s a strategic decision that can lead to improved product quality, reduced waste, and ultimately, a stronger bottom line.